What OEMs Must Know About Cable Testing Standards
Share Article:
OEMs depend on electrical assemblies to keep equipment running reliably. These assemblies face stress from vibration, moisture, temperature changes, and constant use. If they aren’t tested to the right standards, failures can lead to downtime, warranty claims, and safety issues in the field.
Cable testing standards provide a clear framework for quality. They help manufacturers catch defects during production and confirm that each assembly meets performance requirements. For OEMs, this supports consistency across builds and makes it easier to meet customer expectations.
Why Cable Testing Standards Matter for OEMs
OEMs are expected to deliver reliable products at scale. Electrical assemblies are often treated as a small part of the system, but when they fail, the consequences can be wide-ranging. One loose connection or shorted wire can cause full system shutdowns, hard-to-trace errors, or even safety hazards.
Using established cable testing standards helps avoid these issues. These standards give manufacturers clear targets for electrical performance, mechanical strength, and insulation quality. They also make it easier to validate supplier quality and maintain traceability across production.

For OEMs working under strict delivery schedules and compliance requirements, standardized testing keeps projects on track. It reduces rework, lowers the risk of field failures, and helps teams focus on innovation instead of troubleshooting.
Understanding Cable Assembly Testing Basics
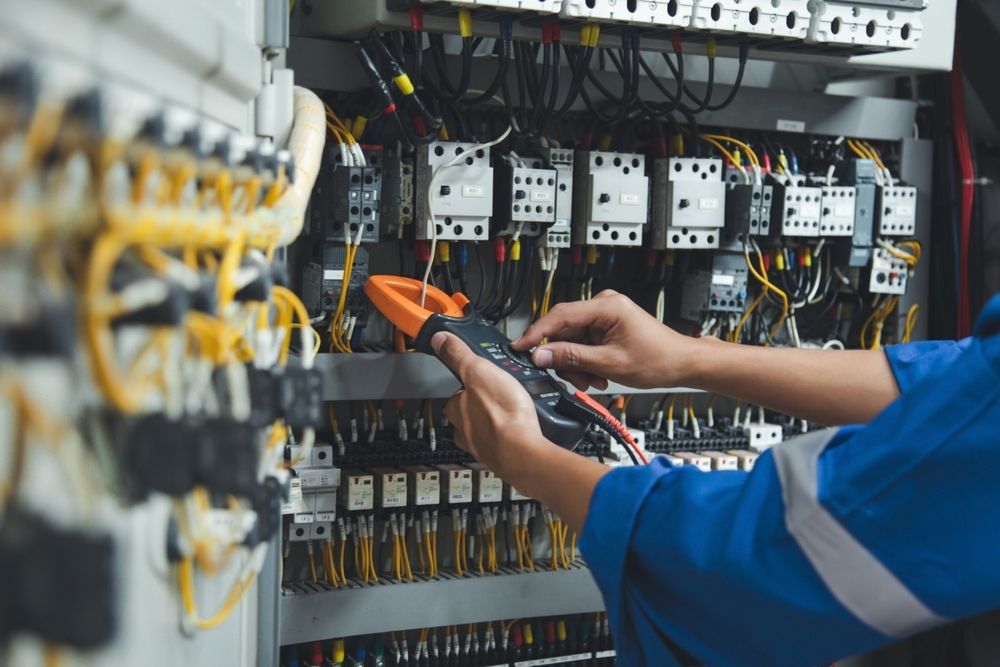
Cable assembly testing checks the electrical and mechanical integrity of the entire build. This includes each wire, connector, terminal, and contact point. The goal is to confirm that the assembly functions exactly as intended before it reaches the customer or end product.
Common testing methods include:
Continuity Testing: Confirms that each circuit is complete and free of open connections.
Insulation Resistance Testing: Measures the resistance between conductors to verify proper insulation.
Hi-Pot (High Potential) Testing: Applies a high voltage to detect potential breakdowns in insulation.
Pull Testing: Evaluates mechanical strength at crimped or soldered connections.
Visual Inspection: Checks for cosmetic defects, correct labeling, and proper routing.
These tests are often automated, especially in high-volume production, but manual checks still play a role in verifying workmanship. The right mix of automated and hands-on testing depends on the assembly’s complexity, the end-use environment, and the customer’s requirements.
Key Industry Standards Every OEM Should Know
Electrical assemblies used in commercial and industrial equipment must meet specific industry standards. Each standard outlines performance requirements, testing methods, and inspection criteria that support reliability and consistency in production. OEMs that follow recognized benchmarks can streamline audits, align expectations with suppliers, and reduce the risk of failures in the field.
IPC/WHMA-A-620
IPC/WHMA-A-620 is one of the most commonly referenced standards for cable and wire harness assemblies. It defines acceptability criteria for soldering, crimping, insulation, labeling, and mechanical performance. This standard is developed jointly by IPC and the Wire Harness Manufacturers Association, making it highly relevant for OEMs that require consistent workmanship across builds.
The standard includes three defined classes based on end-use requirements:
- Class 1: General electronic products
- Class 2: Dedicated service electronics
- Class 3: High-performance electronics where continued performance is required, such as emergency systems or industrial controls
For OEMs, referencing IPC/WHMA-A-620 provides a clear, shared quality standard that can be used across multiple production sites and supply partners.
ISO 9001
ISO 9001 defines the structure for consistent quality management across manufacturing. In cable assembly, it supports traceability, process control, and a documented approach to risk reduction. Each stage of production, procurement, assembly, testing, and delivery is expected to meet measurable standards.
Working with a certified manufacturer helps reduce variation between builds and shows a clear commitment to continuous improvement. It also simplifies audits and helps meet documentation requirements for regulatory or customer approvals.
UL
UL certification focuses on product safety and performance. In cable assembly manufacturing, this often applies to flame resistance, insulation integrity, and material traceability. UL-listed components must meet specific testing standards before they can be used in assemblies labeled for compliance.
Assemblies built with UL-recognized parts and processes can speed up product approvals and reduce liability concerns. Many end customers require UL compliance as part of their product specification, especially in applications involving power distribution or harsh environments.
The Risks of Ignoring Proper Testing Protocols
Inconsistent or incomplete testing introduces risk across production and field performance. Failures tied to electrical assemblies can lead to downtime, lost revenue, and safety concerns.
Key problems include:
Field failures:
Loose terminals, short circuits, or weak insulation can interrupt operation during standard use.
Warranty claims: Assemblies that are shipped without proper verification are more likely to be returned due to performance issues.
Slow diagnostics: Cable-related faults buried within larger systems take longer to identify and resolve when quality hasn’t been confirmed up front.
Compliance issues: Missing records or unclear test methods make it harder to pass inspections or meet customer standards.
Loss of confidence: OEMs that experience repeated issues may see fewer orders, tighter oversight, or even contract termination.
How Evolving Standards Impact Modern OEM Production
Modern equipment demands more from electrical assemblies. Higher voltages, tighter spaces, and new materials require updated testing methods and documentation. Industry standards continue to shift to match these changes.
Manufacturers that follow the latest requirements avoid rework, simplify audits, and keep pace with customer expectations. Staying current helps prevent delays and keeps production moving.

Partnering With Experts for Reliable Interconnect Solutions
OEMs need more than a supplier; they need a partner that understands the technical demands of cable assembly production. A qualified manufacturer brings experience, testing capabilities, and quality systems that align with complex build requirements.
Kato Cable works directly with engineering teams to meet specifications, apply the correct testing standards, and deliver
assemblies that perform under pressure. Every build is handled with precision to match field conditions and customer expectations.
Ensure Compliance and Performance With Kato Cable
Electrical assemblies play a direct role in how equipment performs. Meeting industry testing standards isn’t optional; it’s a necessary part of building reliable products that meet customer and regulatory expectations. Kato Cable brings the processes, experience, and technical knowledge needed to meet these standards without delay or guesswork.
If you're looking for a manufacturing partner who understands compliance, consistency, and production demands, connect with our team.
Request a quote or follow us on LinkedIn and Facebook to start the conversation.